I was asked recently about sherry and it reminded me of a story I wrote one hundred million years ago in 2011 for the Los Angeles Times Magazine. The publication has since closed (not the LA Times, just the magazine) and the story is no longer online, but I scooped it from the Internet Wayback Machine so I could share it again here. (As far as I know the information is still current.)
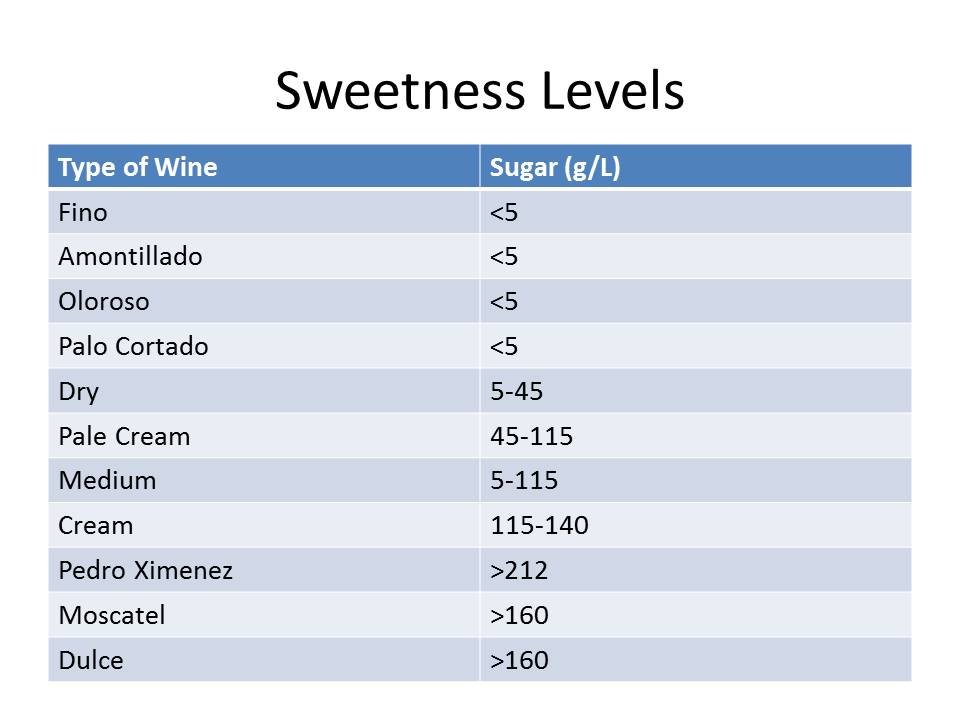
I think it offers a concise overview of the sherry category. And after you read it, check out this set of cool charts on sherry I made here, as it displays the information in easy visual form. I know you people hate reading.
FEBRUARY 2011
Los Angeles Times Magazine
Sherry, Reconsidered
Camper English
As a wine category, sherry has practically everything going for it: a tremendous range of flavors, a rich history dating at least as far back as the Romans, the ability to pair magnificently well with food and an increasingly hip status as a cocktail ingredient used by top bartenders.
Most people, when they think of sherry at all, consider it an ingredient their grandmothers cooked with rather than something ripe for sipping on its own. Sherry is about due for a comeback, but it’s so unfamiliar to us now that it really needs a thorough reintroduction.
SPANISH BODEGAS
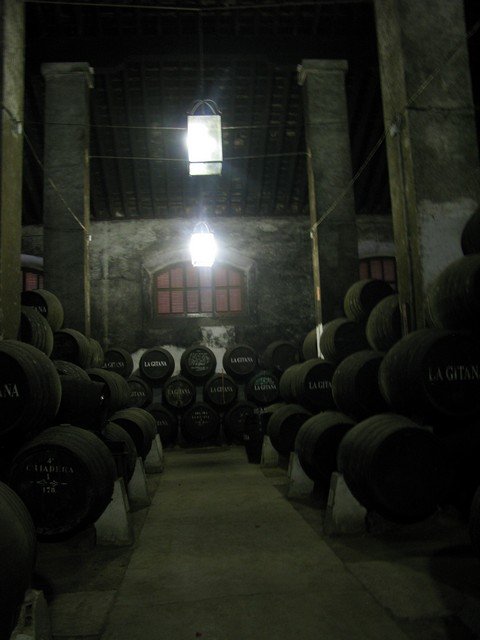
In the three main cities of the delimited sherry region in the southern corner of Spain next to the Atlantic—inland Jerez de la Frontera, coastal El Puerto de Santa María and Sanlúcar de Barrameda—sherry remains both big business and a tourist attraction. More than 230,000 people visit the González Byass each year to ride the miniature train around the bodegas. At Grupo Estévez, visitors browse a gallery filled with Picasso sketches. At Williams & Humbert, they sit for a horse show inside a bodega so large you can’t see one end from the other.
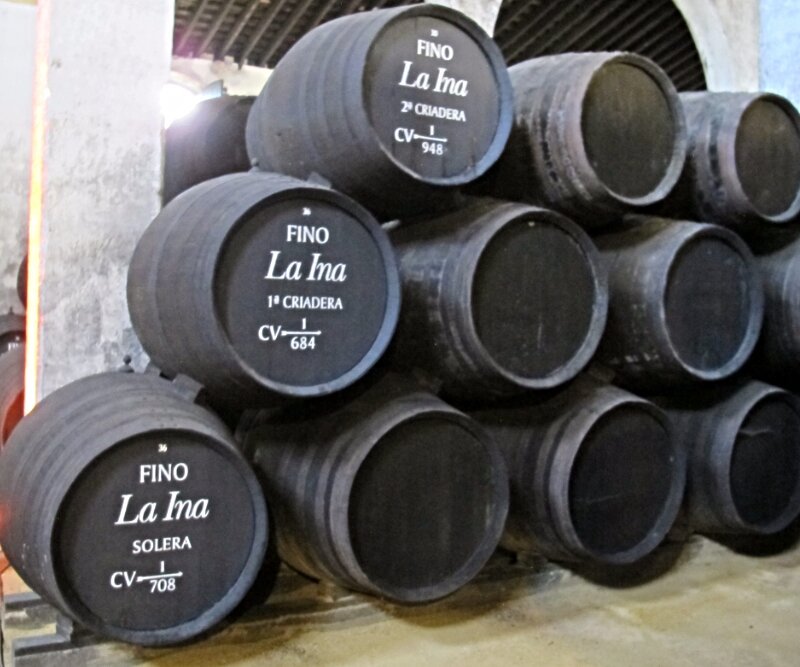
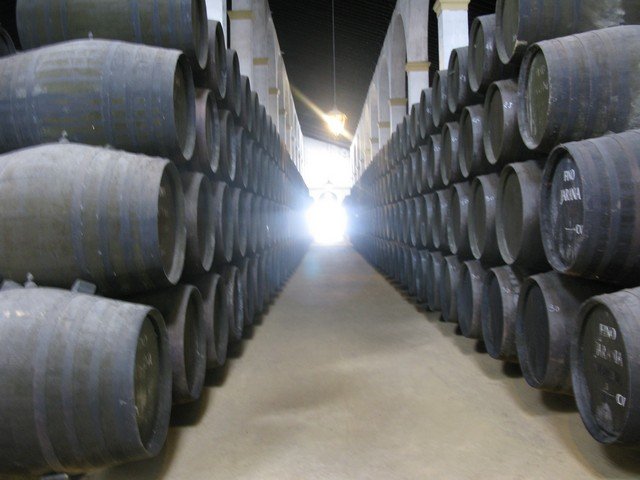
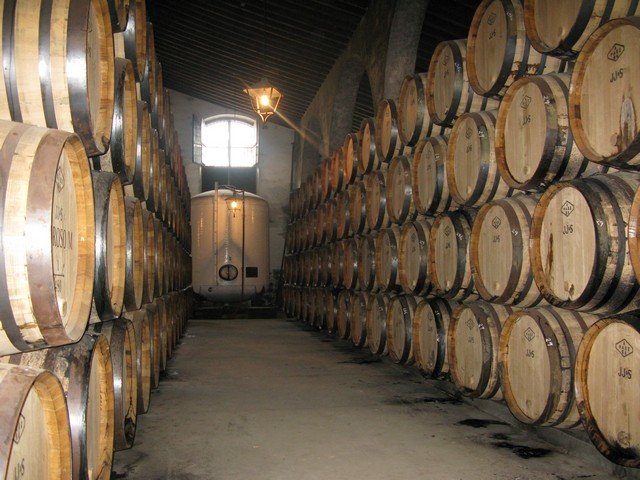
Unlike the vineyard-adjacent grand mansions of California’s wine-tasting rooms, sherry bodegas are usually urban warehouses that may or may not be attached to a visitor’s center. Inside, hundreds to tens of thousands of barrels, usually no more than four high, are stacked on their sides beneath vaulted cathedral ceilings that help stabilize the temperature. The wines will be transferred over the years from the top-row barrels down to the ground-level ones, blending with the wine in each lower barrel in a method known as the solera system.
THE SOLERA SYSTEM
Like port and Madeira, sherry is a fortified wine—meaning distilled spirits are added. Historically, these coastal wines were largely produced for export and needed extra alcohol to survive the sea voyages to Holland, England and America without spoiling. (Christopher Columbus and Magellan both loaded up on sherry before setting sail; Sir Francis Drake allegedly sacked Jerez to get it.)
Until the early 1800s, sherry was heavily fortified and unaged. But around that time, wine traders began experimenting with methods of aging and edification that resulted in the solera system, which is still in use.
Through blending and aging that’s designed to produce a consistent product with characteristics of older wine, the system is almost mathematic. Consider a barrel of three-year-old wine that is ready to be bottled. Instead of emptying the barrel into bottles, only a third of the liquid is used, and the barrel is then filled with wine from a two-year-old barrel; the space in the barrel of two-year-old wine is filled with wine from a one-year barrel; and to the empty space in the one-year-old barrel, new wine is added.
The next year, when the wine is ready for bottling, two-thirds of the barrel will be four years old and a third of it will be three. The following year, after one third of that barrel is removed and refilled as before, there will be three-, four- and five-year-old wine in the barrel—and in the bottle. Run this system for 100 years or so, and some tiny portion of very old wine will be sharing space in the bottle with three-year-old juice.
Because of this (admittedly highly simplified in this description) continuous blending system, sherry should not vary wildly from year to year, and there can be no vintage solera sherry, because it is always a blend of years (though there is a small category of vintage-dated sherries aged outside of the solera system called añadas). Even the newly approved age-dated sherry (VOS, VORS) of 20 and 30 years are average ages based on a complicated algorithm.
THE MAGIC OF AIR AND YEAST
Sherry is made in three styles: dry, sweet and blended. The sweet wines are made from Pedro Ximénez—often known as PX—and muscatel grapes. The grapes are left out in the sun after harvest to further concentrate their sugar, and their fermentation process is halted early to ensure the resulting wines are sweet. The wines are then fortified and aged in the solera system.
These naturally sweet wines can be blended with the five types of dry sherry (fino, manzanilla, palo cortado, amontillado and oloroso) to make wines classified as medium (the brand Dry Sack is a medium sherry) or cream (like Harveys Bristol Cream, the top-selling sherry in America). Yet another type of blended sherry is pale cream, which is fino or manzanilla sweetened with concentrated rectified grape must instead of other sweet wines.
Then there are the dry sherries. The five types mentioned above are all made from palomino grapes (since recovering from a phylloxera infestation in the early 1900s) and aged in barrels by the solera through radically different methods: under air so the wine oxidizes, under a layer of yeast called flor or a combination of the two.
After fermentation, the winemaker decides the aging method for the sherry. The juice destined for aging under air—to become oloroso—is fortified to around 18 percent alcohol as it enters its solera cycle. The barrels, which rest on their sides, are not completely filled, to increase air contact with the wine and change its flavor over time. As it ages, oloroso becomes darker and woodier, with walnut and autumn-leaf flavors.
While oxidative—or air—aging is the muscle that directs the flavor of some sherries, flor is the magic. Flor is a living layer of yeast in the barrel that floats on top of the wine and consumes nutrients within it. (Wine destined for aging under flor is fortified to only about 15 percent alcohol, which permits the flor, but not other organisms, to live.) Not only does this impart pungent, doughy flavors to the wine, the layer of flor prevents the wine from oxidizing like an oloroso.
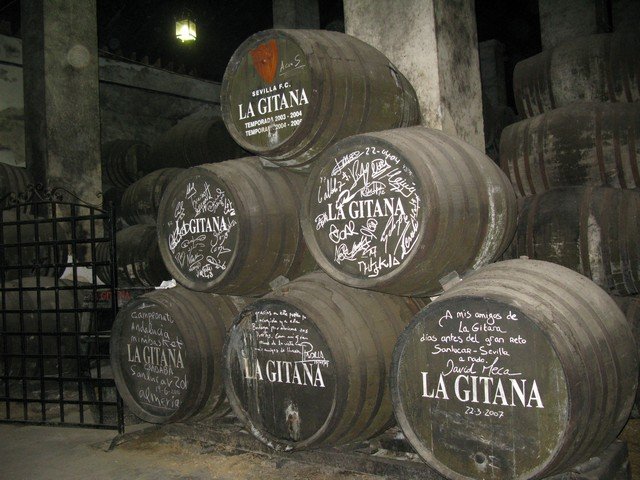
Wines that age entirely under flor are classified as fino or manzanilla sherries. These differ not just in flavor but in where they are aged: Manzanilla comes from the ocean-adjacent Sanlúcar de Barrameda, where salty ocean air affects the aging environment of the barrels and the makeup of the naturally occurring flor. It cannot be replicated elsewhere. The top-selling finosherry brand in the U.S. is Tio Pepe, and among the top manzanilla brands is La Gitana.
These sherries, aged entirely under flor, taste nothing like oloroso sherries that are aged entirely under air. Except for the solera system binding them together, these sherries are as distinct as red and white wine. Following this analogy, the two remaining dry-sherry categories are analogous to rosé wines, with production and flavor characteristics of the other two styles. Amontillado sherries are aged under flor for at least three years (often several more), then the flor either dies naturally or is eliminated, and the wine continues aging through oxidation.
Palo cortado sherry spends less time under flor and is redirected to oxidative aging earlier on. Traditionally, these wines were oddball finos salvaged by redirecting them toward olorosos, but with better technology, this method is deliberate and no longer a happy accident. Each bodega interprets palo cortado differently, putting their house signature on the style. Palo cortado is often the focus for sherry obsessives.
MIXING IT UP
Adventurous cocktailians in the States use any type of sherry at their disposal—and have been doing so pretty much for more than 200 hundred years—while in Jerez, about the only cocktail you’ll find with sherry is the rebujito, a mixture of fino or manzanilla sherry with Sprite.
Classic sherry drinks include the Sherry Cobbler (sherry with sugar and muddled fruit and berries), the Adonis (with sweet vermouth and bitters), Bamboo (with dry vermouth and bitters) and Coronation (a Bamboo with maraschino liqueur). Not only does sherry pair with vermouth in low-alcohol cocktails as above, it can sub in for either dry (fino/amontillado) or sweet (oloroso) vermouth in drinks like the martini and Manhattan.
These classics pop up on cocktail menus from time to time, as do new creations like the Dolly Dagger at the Varnish (dry sherry, rum, lime juice, sugar-cane syrup, vanilla syrup) and the Bomb at Seattle’s Zig Zag Café (amontillado sherry, triple sec, orange juice, bitters).
For those who want their sherry unadorned, serving directions are simple. No need for the special sherry copita; a white-wine glass will do nicely. Chill the fino and amontillado down to slightly above refrigerator temperature, and serve the others at slightly below room temperature. In Spain, a grand meal often begins with a subtle fino, moves into oloroso to pair with the main course and ends with sweet, rich Pedro Ximénez with (or for) dessert. ¡Salud!
Should you choose to serve sherry in cocktail form—perhaps one of the sherry drinks featured in these pages, which were developed by top bartenders from around the country—you’ll find them as diverse as the flavors in sherry itself. Maybe sherry skipped a generation, but now you and your grandparents have something in common.
Recipes
THE BOMB
by Murray Stenson
Zig Zag Café, Seattle
“From the 1977 Jones’ Complete Bar Guide, by Stan Jones. It’s on our current drink menu and is unique and delicious.”
• 1 1/2 ounces amontillado sherry
• 1/2 ounce Cointreau
• 3/4 ounce orange juice
• 1 dash orange bitters
• 1 dash St. Elizabeth Allspice Dram
Combine ingredients in mixer with ice and shake. Strain into cocktail glass. Serve without garnish.
PÉTANQUE
by Andrew Bohrer
Mistral Kitchen, Seattle
“I like to make delicate flavor balances tailored especially for mood and food. it would be perfect with a charcuterie plate. This was created to show the adaptability of sherry.”
• 2 ounces fino sherry (Toro Albalá Fino Eléctrico)
• 1 ounce Luxardo Amaretto di Saschiro liqueur
• 2 dashes Peychaud’s bitters
• Luxardo Maraschino cherry for garnish
Combine ingredients in a mixing glass, stir with ice and strain into grappa glass. Garnish with cherry.
SHERRY SHRUB
by Neyah White
Nopa, San Francisco
White, currently brand ambassador for Suntory Yamazaki whisky, created this drink, which won the prestigious Vinos de Jerez Cocktail Competition in 2008. It has been influential as bartenders have begun making their own shrub syrups with local produce. Shrub syrup is a colonial-era preservative (a liquid jam, in a way) that’s drinkable with soda water or used in cocktails in place of the acid ingredient. “The beauty of this cocktail,” White says, “is seasonality and custom flavors; it should be made with whatever produce is peaking that week. The base recipe is equal parts sugar, vinegar and cut fruit. The sugar-to-acid ratio varies by the sugar of the fruit.” White has made this with plums, peaches, apples, pears, strawberries, grapes, rhubarb, quinces, persimmons and beets. “I never use melons, citrus or pineapples, as there are some sanitation issues with aging those fruits.”
• 3⁄4 ounce shrub syrup*
• 2 ounces Bodegas Hidalgo La Gitana manzanilla sherry
• Lemon twist for garnish
Combine sherry and syrup, stir with ice and strain into small sherry glass. Garnish with lemon twist.
*Shrub Syrup
• 1 quart fresh elderberries, trimmed from stems
• 1 cup fresh huckleberries
• 5 cups evaporated cane sugar (available at Whole Foods)
• 1 quart cider vinegar
• 1 ounce kosher salt
• 5 brown cardamom pods
• 1 ounce white peppercorns
In a large bowl, gently press fruit with the bottom of a metal shaker, until every berry is at least bruised. In mixing glass, muddle spices until all pods are cracked and add to berry mixture. Add sugar, cover and let stand five hours in a cool place—refrigerate if preferred—until a syrup has formed. Add salt and vinegar and stir until salt has dissolved. Cover and return to cool storage. Let age for at least a week. To remove seeds, filter successively through a chinois (china cap) and then through cheesecloth. Bottle in sterile glass containers, leaving a few inches of air. It is now ready to use, but another week of aging allows for a more lingering flavor.
SMOKED PEACH
by Kevin Diedrich
Burritt Room, San Francisco
“I chose sherry for this drink because it gives it a nice nutty flavor—kind of a stone-fruit aspect. Also, it dries out the sweetness of the honey and peaches. The cocktail is in balance, matching scotch and honey, sherry and scotch and peaches and honey. I almost didn’t have to do any work with this—it just came together naturally!”
• 1 1/2 ounces Dry Sack Medium sherry
• 1 ounce Glenfiddich 12-year-old scotch
• 1/2 ounce honey syrup*
• 3/4 ounce lemon juice
• 4 thin peach slices, plus extra slices for garnish
Muddle sliced peaches into mixing glass. Add liquid ingredients and shake with ice. Strain into rocks glass with ice. Garnish with peaches presented in a fan shape.
*Honey Syrup
Dilute one part honey with half part of hot or boiling water. Store in capped bottle in the refrigerator.
O.G. (ORIGINAL GIN)
by Zahra Bates
Providence, Los Angeles
“I roast red grapes that I then add to the sherry to evoke a mulled-wine flavor. Sherry is a great way to add warmth to a cocktail without creating a cloying, sweet taste.”
• 2 ounces Bols Genever
• 1 ounce red-grape sherry reduction*
• 1 ounce Lillet Blanc
• 1 dash anise bitters or 1⁄2 teaspoon Pernod
• Orange peel for garnish
Combine liquid ingredients in an ice-filled mixing glass and stir until well chilled. Garnish with flamed orange oil: Hold quarter-size orange peel in your fingers and squeeze it with peel side facing cocktail about six inches from glass, with lit match in front of the peel.
*Red-Grape Sherry Reduction
• 1 pound red grape, preferable Kyoho
• 1/3 bottle dry sherry
On baking sheet, roast grapes at 350 degrees with a bit of salt and no oil or grease of any kind for 11–15 minutes. Grapes are done when they split and juices start running out. Muddle grapes in saucepan and add sherry. Bring to a boil, lower heat and simmer until reduced to about half the volume. Strain out the solids and let liquid cool. Store in refrigerator.
EAST INDIA TRADING COMPANY
by Brian Miller
Death + Company, New York
“I was playing around with making some classic cocktails with rum. I got inspired by the Boulevardier and the Negroni, and this establishment was a nice little twist on it. I won the NYC semifinal for the AppletonReserve Remixology contest with this one, and it’s still on the Death + Company menu.” Miller recently left the bar and is currently consulting.
• 2 ounces Appleton Estate Reserve rum
• 3/4 ounce Lustau East India Solera sherry
• 1/2 ounce Ramazzotti
• 2 dashes Bittermens Xocolatl Mole Bittersh
Combine all ingredients, stir with ice and strain into chilled cocktail glass. No garnish.
RED BAMBOO
by Kenta Gogo
Pegu Club, New York
“This is my way to reintroduce the Bamboo, a clean, dry aperitif cocktail—the first cocktail created in Japan. It sometimes is nice to step away from hard liquor. I was picking apples somewhere in Hudson Valley on my birthday last year, and everything just came into my mind—add fall essence to give the drink a whole brand-new face without losing the fundamental structure. A modern twist on classic.”
• 2 ounces Eve Apple vermouth*
• 1 ounce Harveys Bristol Cream
• 1⁄2 teaspoon Drambuie
• 3 dashes absinthe
• 1 dash Angostura bitters
• Apple slices for garnish
Combine all ingredients and stir with ice until well chilled. Strain into a small chilled cocktail glass. Garnish with apples presented in a fan shape.
*Eve Apple Vermouth
by Audrey Saunders
Pegu Club, New York
• 1 liter Dolin dry vermouth
• 8 McIntosh apples
In a nonreactive container, slice apples deli thin and add vermouth. Cover and chill 5 days. Strain and store in refrigerator.
DOLLY DAGGER
by Alex Day
The Varnish, Los Angeles
“I started playing around using sherry as a base and other spirits as modifiers, inverting the ratio that most people use in cocktails. I made it into a swizzle, because I felt Smith & Cross was so aggressive that using crushed ice and getting it super cold had the ability to round out the flavor better. I also like using mint only as an aromatic component of a drink.”.
• 1 1⁄2 ounces Dry Sack sherry
• 1 ounce Smith & Cross rum
• 3⁄4 ounce lime juice
• 1⁄2 ounce sugar cane syrup
• 1 teaspoon vanilla syrup (homemade or Trader Tiki’s)
• Mint sprig for garnish
Combine ingredients in cocktail shaker and shake without ice. Pour into pilsner glass filled with crushed ice. Swizzle until outside of glass is frosted. Garnish with mint sprig.