Way back in February I took a quick trip to Mexico to visit the distillery La Cofradia, where they make Casa Noble tequila. They make other brands there too, but I was there as the guest of their flagship brand Casa Noble.
A Beautiful Distillery
La Cofradia is located about a mile outside of the town of Tequila in the Lowlands of Mexico about 45 minutes outside Guadalajara. In Mexico a few distilleries cultivate a garden-like environment but here they take it to another level. There is a central courtyard with trees, a duck pond, a little cafe, and a set of four cottages where visitors like me can stay.

Casa Noble Tequila Production
Casa Noble is a certified organic 100% agave tequila. In order to be organicaly certified you need to prove that the land has been organically farmed and not had chemicals used on it for a certain number of years. Casa Noble avoided that problem by purchasing virgin land in Nayarit and planting fresh agave there. Nayarit is one of the five states where it is legal to grow agave, though nearly all of it comes from the state of Jalisco where the distillery is located.
Thus Casa Noble uses estate-grown agave. This is a growing trend in the tequila industry; producers owning or renting the agave fields so they can control the both the care and harvest of it, but also the price, avoiding the dramatic gluts and shortages of agave in the industry as a result of its long, 6-11 year growing cycle.

(Agave pina (pineapple))
The fields in Nayarit are at an elevation of about 4000 feet, higher than some of the Highlands. Yet the agaves I saw at the distillery were much smaller than Highland agave I've seen. Those are often 200 pounds compared with the 110 pound or so average at Casa Noble (and thus only had to be split in half before baking; some Highland producers split theirs into quarters). They purposefully chose an isolated location for their fields, because they are organic: they wouldn't want airborne agave diseases to spread to their fields.
After harvest, the agave pinas are brought to the distillery where they'll be baked, shredded, fermented, and distilled. Baking converts the complex sugars in the agave into simpler, fermentable sugars.

(Closeup of piece of agave. You can see the fibers. The sugars are stored between these fibers which is why agave is shredded after baking to release them.)
Baking and Shredding
La Cofradia has 5 hornos (ovens), 3 large 40-ton ones and 2 smaller 20-ton ones. The agave is steam baked for 36-38 hours. Then it cools before the next step. They hasten the cooling process by using large fans blowing through the two sides of the oven.
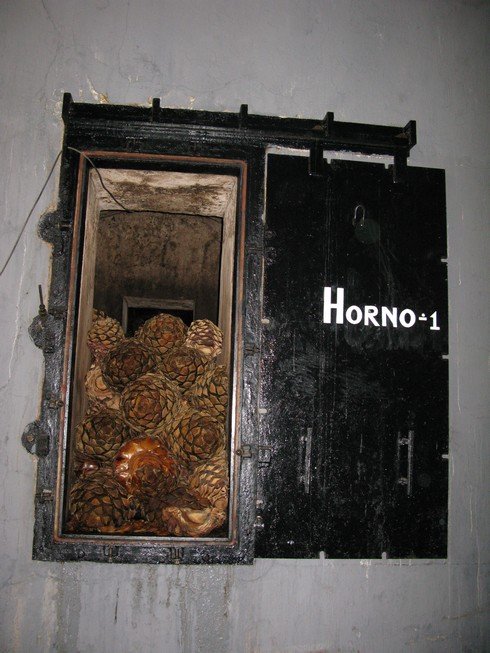

When agave is cooking with steam, the first water than runs off the bottom is called "bitter honey" and it is discarded. The next mass of water is called the "oven honey" and this is collected. We sampled this water- its sweet, watery, and has a vinegar note to it. (David Yan, Marketing Director there, says he's used a refined version of this as a vinegrette on salads.)
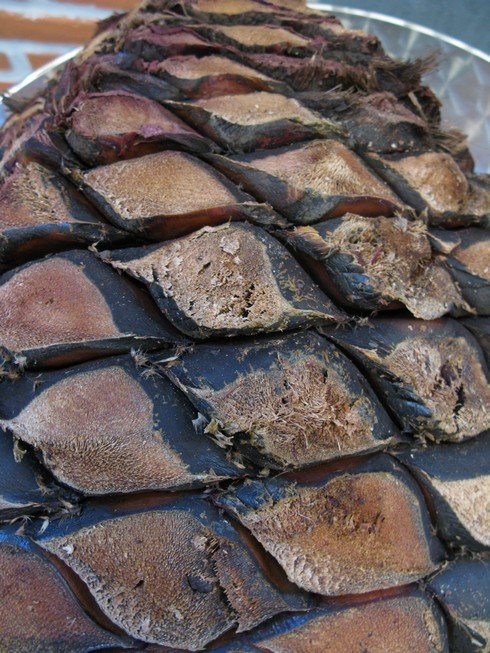

(Baked agave.)
After baking the agave is shredded to expose the fermentable sugars that can be washed out and fermented. At La Cofradia they have a unique system: First the baked agave pinas are put through a sort of wood chipper (not a roller mill) with water. This water is collected and they call it the "fat extraction."
Next the chipped agave goes into a two "extractors" that are shaped like horizontal metal tubes. The first part of the extractor is like a corkscrew that compresses the fibers in the agave. Then it passes through to a set of paddles on a central axis that spins the agave fibers outward and washes them with water. Apparently this helps separate the fibers without neccesarily shredding them.
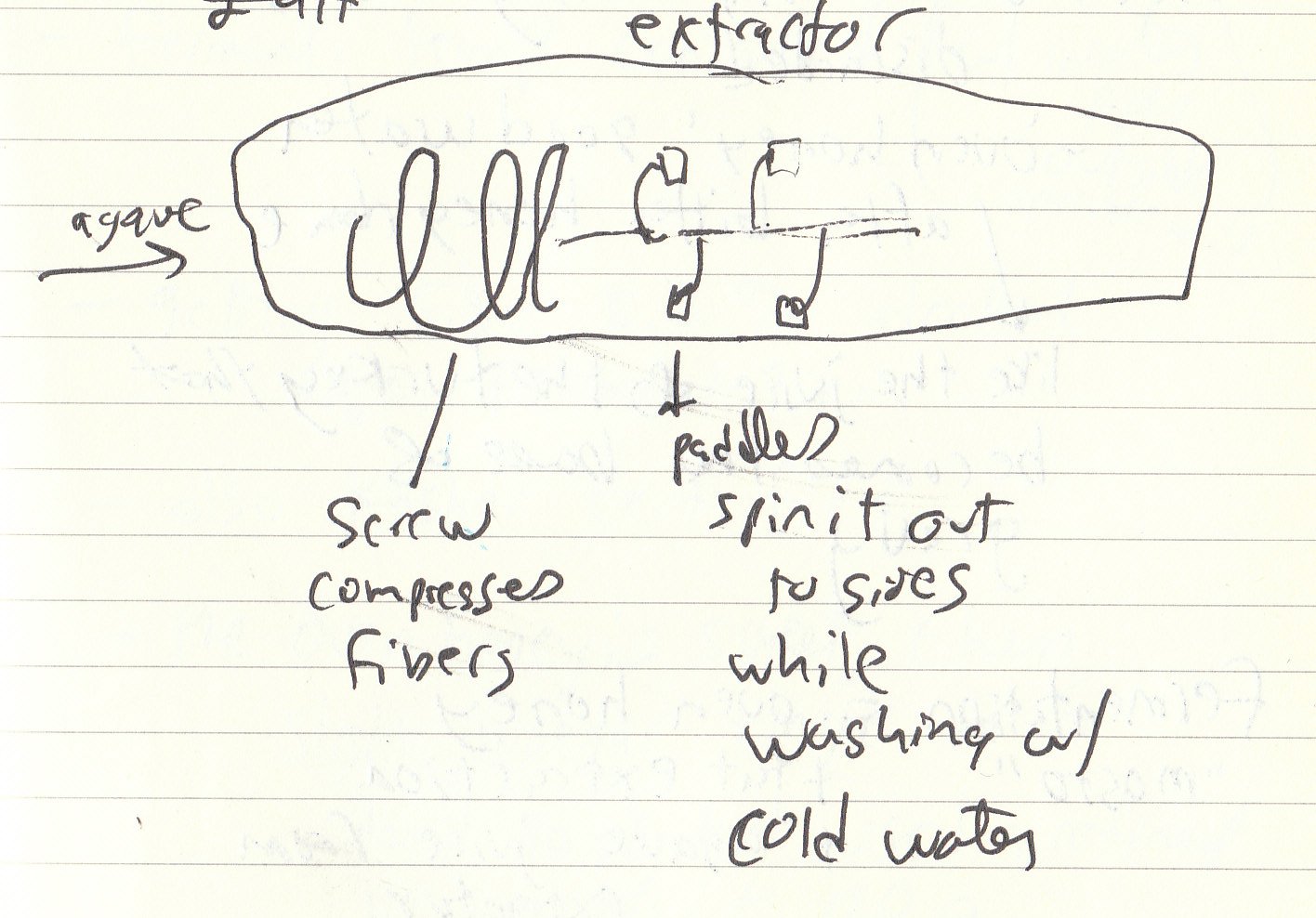
(Diagram of extractor from my notes.)
Fermenting and Distilling
Now, onto fermentation. They ferment the combination of the oven honey, fat extraction, and agave juice from the extractors. Yeast is added that feeds on the fermentable sugars and converts it into alcohol plus CO2. While filling the fermentation vats, they bubble air into the tank, which they say makes the yeast reproduce more. This increases their alcohol conversion by an extra 1-2%.

(Ready for fermentation.)
After fermentation (3-5 days, depending on the time of year), the yeast has died and the juice is called "mosto muerto." Now it's time to concentrate the alcohol through distillation.
At La Cofradia they have large and small stills for the first and second/third distillations. The first, large stillas are called "destroyers" and their job is to get rid of most of the heads and tails.The resultant spirit is 22% alcohol.

(Destroyer stills closer, smaller stills further away.)
The smaller stills are used for both a second and third distillation that refine the spirit. Though the first distillation cuts most of the heads and tails, there are smaller cuts on the second and third distillations. Both bring the alcohol to 55% ABV. (For most of the other brands that are produced at La Cofradia, they distill only twice. As this is the flagship brand they refine it more.)
After distillation (or, in the case of the aged tequilas, after aging) the tequila is filtered through micro-cellulose fibers and diluted to proof. The blanco (only?) is oxygenated before bottling for 8-12 hours.
Aging and Tasting
The barrels for aging Casa Noble come from the Taransaud cooperage in France. They're new French oak with a light #1 char, and nobody else in Mexico uses these barrels.The tequila goes into the casks at 55% ABV from the still (not watered down before barreling).

(New French oak barrels.)
Interestingly, the tequila destined to be anejo (minimum 1 year aging) goes into new casks. The reposado (2 months to 1 year aging) goes into refilled caks. (More often, brands will use newer casks for reposado tequilas and older ones for anejo so that the wood affects the spirit more in a shorter time for the reposado.) They refill these casks for reposado 7-8 times.
Cristal/Blanco: This tastes of nickel and minerals, white and red pepper, and "agave sticks" according to my tasting notes.
Reposado: The reposado is aged for 364 days, the maximum amount before it would be in the anejo category. Reposado is aged in all 228-liter barrels. My tasting notes were: Boo-berry, strawberry cream popsicle, and white flowers.

(Tasting.)
Anejo: Here's where Casa Noble separates itself from the pack yet again. Though all barrels are new French oak from Taransaud, they actually use three different sizes of barrels: 114 liter, 228 liter (about the size of bourbon barrels), and 350 liter barrels. These are blended together to create the anejo.
The anejo is aged for 2 years. (Anejo is aged a minimum of one year. Extra-anejo starts at three years.) You can definitely taste all three of the below flavor profiles in the anejo.
We were given the opportunity to taste tequila aged in each of the three sizes of barrels, each of them for a little under two years.
114 liter: bitter wood, used peanut oil
228 liter: fruit, dusty Boo-Berry, most similar to the reposado
350 liter: floral, strawberry juice, light
Now, besides Casa Noble, I can only think of one other set of brands that ages their spirit in similar casks of different sizes: Jim Beam. Laphroaig and Ardmore both do "quarter cask" programs.
So, Wow.
This is a distillery that uses traditional methods in many ways (stone ovens, gentle agave processing) yet has built their system from the ground up (new agave fields, agave processing methods, distillation, aging). And it's all done in a lovely setting to which I'd love to return someday.


































































